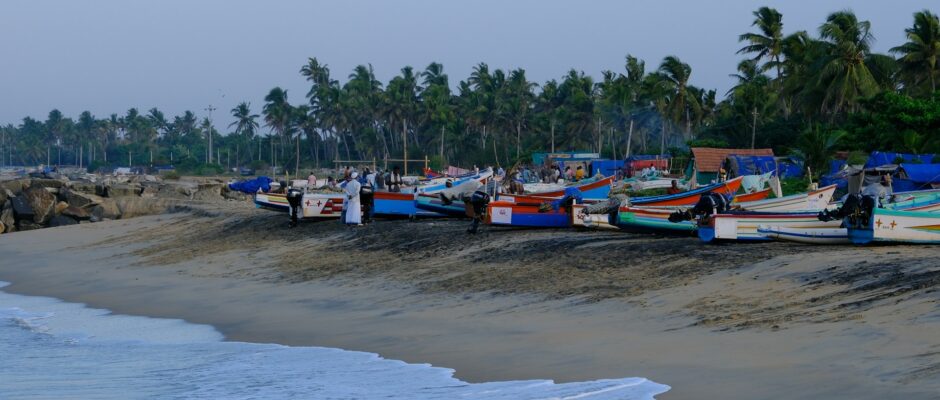
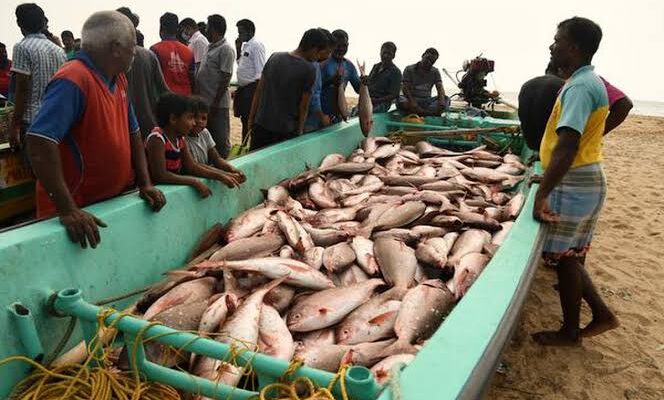
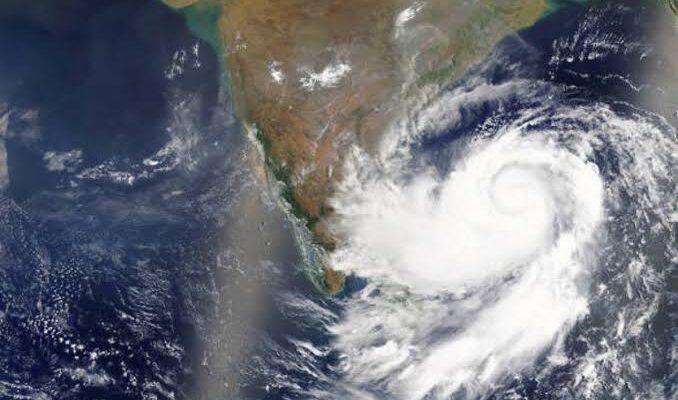
A Market in Flux: US Shrimp Imports Defy Tariffs and Tumult to Achieve Near-Record Volumes in 2025
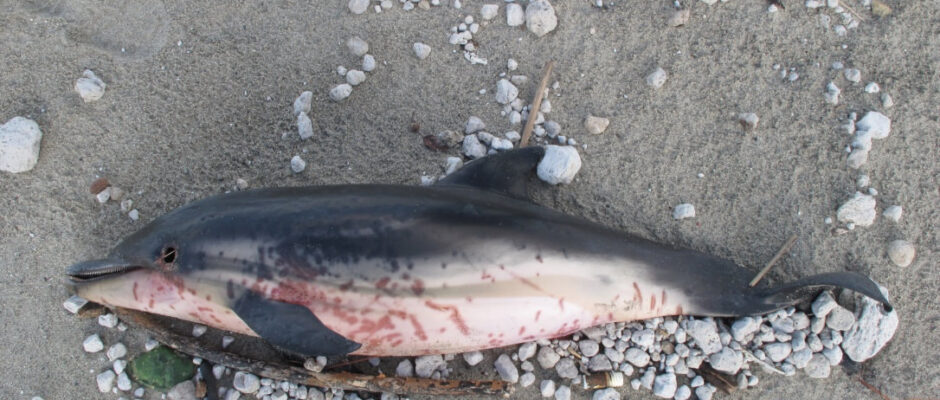
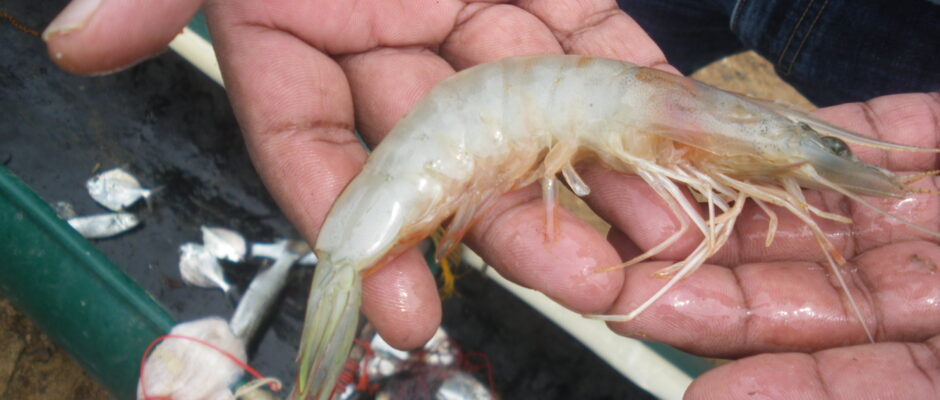
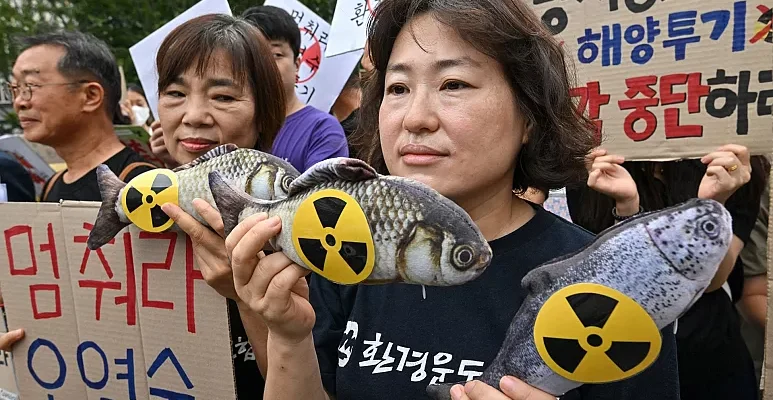
The United States shrimp market proved remarkably resilient in 2025. Despite a barrage of steep reciprocal tariffs, countervailing duties (CVD), and alarming food safety recalls, US importers closed the year with their fourth-largest volume in history. Reaching a total of 795,641 metric tons (MT)—a 2% increase over 2024—the data reveals a complex year defined by aggressive front-loading, geopolitical maneuvering, and dramatic shifts in the global supply chain. Total import value also climbed by 9% year-over-year to $7.03 billion. The 2025 Timeline: A Tale of Two Halves The modest full-year growth masks immense volatility, splitting 2025 into two distinct phases driven primarily by impending trade policies: How the Top Suppliers Fared The shifting trade dynamics forced a major realignment among the “Big Three” suppliers to the US market. 1. India: Retaining the Crown, but Feeling the Squeeze India remained the largest single supplier to the US, shipping 300,051 MT (up 1% YoY). However, this annual stability is deceptive. Following the imposition of a 25% reciprocal tariff—compounded by penalties related to Russian oil purchases and existing anti-dumping duties—the effective tariff rate for Indian shrimp skyrocketed to an estimated 58.26%. While existing orders buffered the impact early in the year, Indian shipments to the US collapsed by 57% in October. This stark reality underscores the urgent need for a pivot in business strategy and exports, accelerating the industry’s push to diversify toward emerging markets like Europe, China, and Vietnam. 2. Ecuador: The Clear Structural Winner Ecuador capitalized heavily on the tariff disparities in Asia. Subject to much lower US tariff rates (around 10–15%), Ecuador surged ahead to reach 231,804 MT in 2025, marking an impressive 18% year-over-year growth. By scaling their headless, shell-on shrimp exports and maintaining cost competitiveness, Ecuadorian producers effectively absorbed the market share left vulnerable by Asian suppliers. 3. Indonesia: Radiation Scares and Trade Hurdles Indonesia finished the year down 11% at 119,331 MT. While initially poised to benefit from India’s high tariffs, Indonesia’s momentum was derailed in the fourth quarter. Severe food safety concerns—specifically the Cesium-137 radiation issue affecting Indonesian shipments—triggered widespread import bans. By December, Indonesian shrimp imports to the US had plummeted by a staggering 72%. Value Outpaces Volume A standout trend from the 2025 data is that the total value of imports (+9%) grew significantly faster than the volume (+2%). This was driven by two key factors: